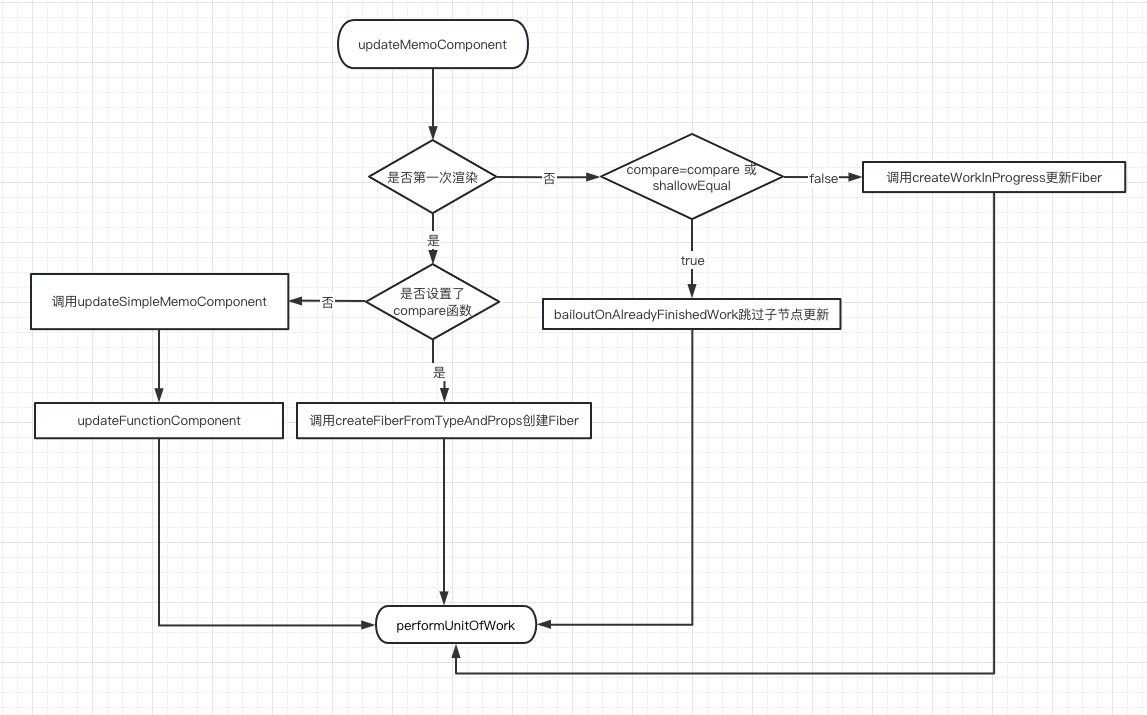
Memo组件的具体一个渲染流程
Memo使用方法
typescript
import React from 'react'
const MemoComponent = () => {
return (
<div>
MemoComponent
</div>
)
}
export default React.memo(MemoComponent)memo函数其实就是创建了一个ReactElement
memo
typescript
export default function memo<Props>(
type: React$ElementType,
compare?: (oldProps: Props, newProps: Props) => boolean,
) {
return {
$$typeof: REACT_MEMO_TYPE,
type,
compare: compare === undefined ? null : compare,
};
}updateMemoComponent
typescript
function updateMemoComponent(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
Component: any,
nextProps: any,
updateExpirationTime,
renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime,
): null | Fiber {
if (current === null) {
// Component 就是React.memo函数返回的那个ReactElement
// type属性就是React.memo包裹的组件
let type = Component.type;
if (
isSimpleFunctionComponent(type) &&
Component.compare === null &&
Component.defaultProps === undefined
) {
// 如果是一个简单的memo函数组件,其实当前memo节点并不会有实质的dom
// 节点的渲染,应该需要调和的是memo包裹的函数组件,所以在这里将type
// 更新到memo的fiber对象上,也就是函数组件和memo函数组件就是公用一个Fiber
workInProgress.tag = SimpleMemoComponent;
workInProgress.type = type;
return updateSimpleMemoComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
type,
nextProps,
updateExpirationTime,
renderExpirationTime,
);
}
// 不符合上面的条件,直接创建Fiber
let child = createFiberFromTypeAndProps(
Component.type,
null,
nextProps,
null,
workInProgress.mode,
renderExpirationTime,
);
child.ref = workInProgress.ref;
child.return = workInProgress;
workInProgress.child = child;
return child;
}
let currentChild = ((current.child: any): Fiber); // This is always exactly one child
if (updateExpirationTime < renderExpirationTime) {
// updateExpirationTime < renderExpirationTime 说明当前函数组件
// 渲染的优先级比较低,并不需要在这次更新中渲染,这个时候会先判断新老props
// 如果没有改变, 那么提前在这一次渲染将这个组件的更新跳过
const prevProps = currentChild.memoizedProps;
// Default to shallow comparison
let compare = Component.compare;
compare = compare !== null ? compare : shallowEqual;
if (compare(prevProps, nextProps) && current.ref === workInProgress.ref) {
return bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork(
current,
workInProgress,
renderExpirationTime,
);
}
}
// 重新渲染Fiber,进行更新
let newChild = createWorkInProgress(
currentChild,
nextProps,
renderExpirationTime,
);
newChild.ref = workInProgress.ref;
newChild.return = workInProgress;
workInProgress.child = newChild;
return newChild;
}updateSimpleMemoComponent
typescript
function updateSimpleMemoComponent(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
Component: any,
nextProps: any,
updateExpirationTime,
renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime,
): null | Fiber {
if (current !== null) {
// 说明不是第一次渲染,这个时候会对新老props进行浅比较
// 如果浅比较相等,也就是新老props没有变化,那么会跳过当前组件的更新
const prevProps = current.memoizedProps;
if (
shallowEqual(prevProps, nextProps) &&
current.ref === workInProgress.ref
) {
didReceiveUpdate = false;
if (updateExpirationTime < renderExpirationTime) {
return bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork(
current,
workInProgress,
renderExpirationTime,
);
}
}
}
// 否则的话,直接调和函数式组件
return updateFunctionComponent(
current,
workInProgress,
Component,
nextProps,
renderExpirationTime,
);
}shallowEqual
- 首先使用is函数判断两个对象是否相等, 这里是严格比较
- 如果不相等,处理null的情况, 两个null是不相等
- 其次在针对两个对象做一个遍历,对比各自的属性是否相等(没有进行递归)
typescript
function is(x: any, y: any) {
return (
(x === y && (x !== 0 || 1 / x === 1 / y)) || (x !== x && y !== y) // eslint-disable-line no-self-compare
);
}
function shallowEqual(objA: mixed, objB: mixed): boolean {
if (is(objA, objB)) {
return true;
}
if (
typeof objA !== 'object' ||
objA === null ||
typeof objB !== 'object' ||
objB === null
) {
return false;
}
const keysA = Object.keys(objA);
const keysB = Object.keys(objB);
if (keysA.length !== keysB.length) {
return false;
}
// Test for A's keys different from B.
for (let i = 0; i < keysA.length; i++) {
if (
!hasOwnProperty.call(objB, keysA[i]) ||
!is(objA[keysA[i]], objB[keysA[i]])
) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}